ADHD – Causes, Symptoms, and Foods to Avoid

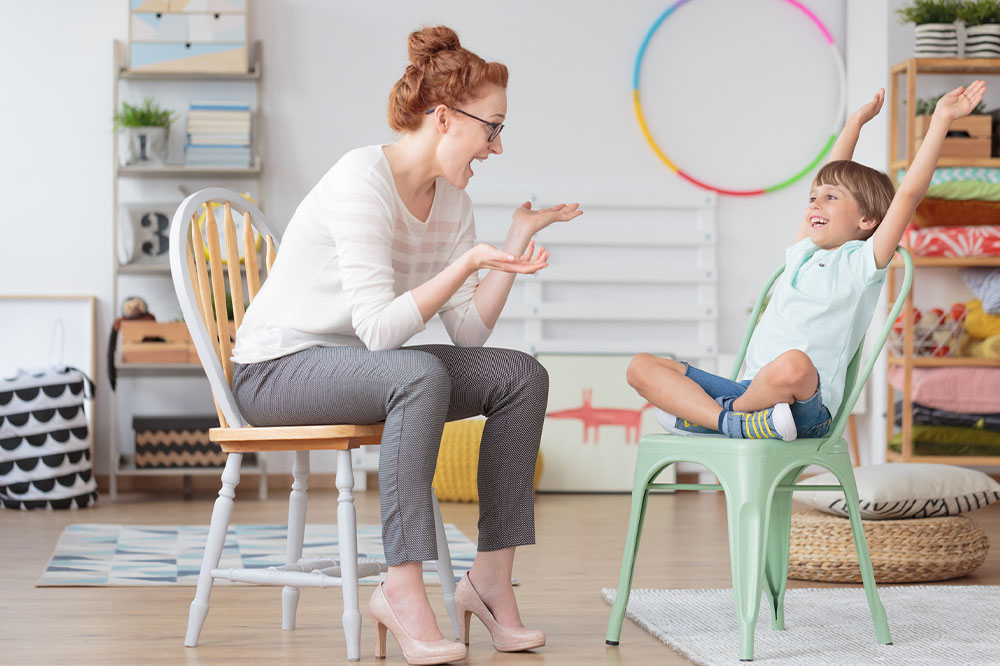
Neurodevelopmental disorders in childhood can challenge children’s intellectual growth and development. Timely diagnosis and intervention are essential to ensure the child’s steady progress. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is among the most prevalent neurodevelopmental conditions, involving difficulty paying attention, severe restlessness, and impulsive behavior. Today, several types of therapies are being implemented to help children with ADHD perform better in the academic and personal spheres. Here’s everything to know about ADHD:
What Causes ADHD?
Genetic predisposition
Adoption studies have shown that genetic factors play a significant role in the onset of ADHD. In most cases, individuals inherit this condition from their parents. About one-third to 50% of children with parents affected by ADHD inherit the disorder.
Brain injury
Children suffering from a severe head injury affecting the brain are likely to develop ADHD. In such scenarios wherein ADHD is caused by trauma, the condition is called secondary ADHD.
Exposure to harmful substances during pregnancy
Studies have shown that the chances of developing ADHD were higher among children whose mothers had been exposed to harmful substances like lead during pregnancy.
Maternal stress and trauma during pregnancy
Children whose mothers have undergone immense stress or trauma while pregnant are susceptible to being diagnosed with ADHD later in life.